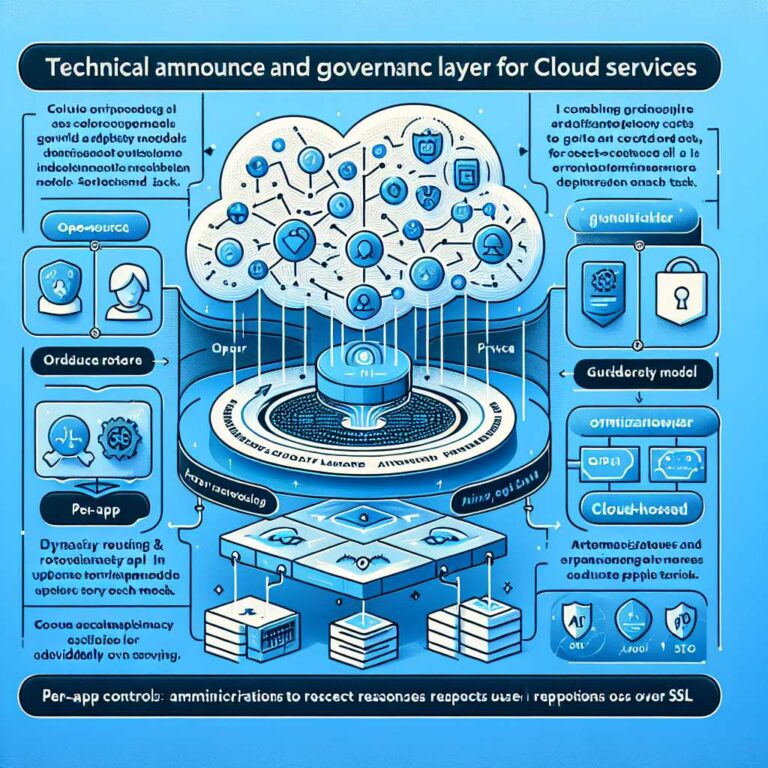
Atlassian has published a detailed look at how Rovo’s artificial intelligence capabilities are built and governed, emphasizing its Responsible Technology Principles. Rovo combines open-source and Atlassian-hosted models, such as Llama and Mixtral, with third-party hosted large language models including OpenAI’s GPT, Anthropic’s Claude, and Google’s Gemini. Features use dynamic routing to select models for each scenario, and Atlassian states that its providers do not store customer inputs or outputs or use them to train their services.
The company explains that Rovo processes user inputs and organizational data that a user is permitted to view in order to generate responses. Customer inputs and outputs are used only to serve and improve individual customer experiences, not to train models across customers, and may be stored temporarily to reduce latency or power features such as search history. Data sent to third-party providers is transmitted individually over SSL in line with Atlassian security practices. Rovo is covered by the Atlassian Customer Agreement and related policies, and the company says it supports GDPR compliance, has completed SOC 2 and ISO 27001 certifications, and offers data residency for in-scope app data. Rovo is not HIPAA compliant at this time.
Admins can manage artificial intelligence features per app in Atlassian Administration, though Rovo Apps are core to the Atlassian Cloud Platform and non-AI capabilities like Rovo Search cannot be disabled. Atlassian currently offers opt-out controls at the app level and provides allowlist or blocklist settings to limit content indexed from Google Drive or Microsoft SharePoint. Customers cannot choose specific model providers because Rovo relies on dynamic routing.
Rovo enforces usage policies by honoring existing permissions across Jira, Confluence, and connected sources, meaning results and generated content reflect only what a user is allowed to access. Two types of connectors are available: admin-managed connectors, which are off by default and respect user permissions, and Smart Link connectors, which require no admin setup and surface results based on an individual user’s permissions and history. Rovo Agents operate within a user’s established access rights, and when agents are invoked via automation, their knowledge access aligns with the permissions of the connecting user.
Atlassian also cautions that some models are probabilistic and may produce inaccurate or incomplete outputs. It encourages users to avoid relying on these features for scenarios requiring current and accurate information about people, places, and facts, and to review responses before sharing.