Foundation models have demonstrated transformative potential in various scientific fields, yet their application in Artificial Life (ALife) research has been limited. Researchers from MIT, Sakana AI, OpenAI, and The Swiss AI Lab IDSIA have introduced the Automated Search for Artificial Life (ASAL) framework, which leverages vision-language foundation models to revolutionize the discovery process in ALife studies.
ASAL is designed to work with various ALife platforms like Boids, Particle Life, Game of Life, Lenia, and Neural Cellular Automata. By using ASAL, researchers are now able to discover previously unknown lifeforms and further extend their understanding of emergent structures within these simulations. The framework allows for quantitative analysis of traditionally qualitative phenomena, and its FM-agnostic design ensures future compatibility.
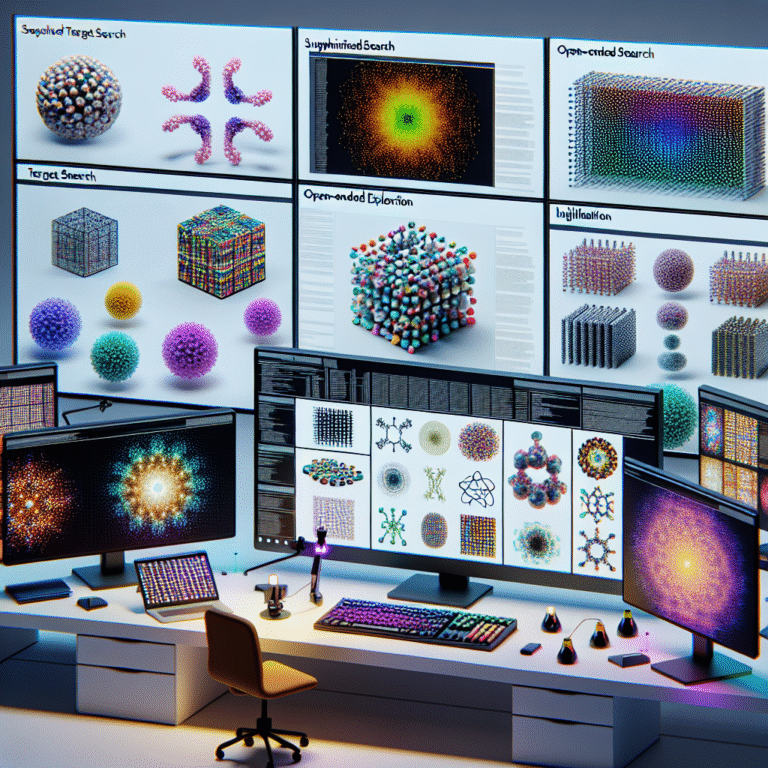
The framework employs three distinct search strategies: Supervised Target Search, Open-Ended Exploration, and Illumination, which respectively align simulations with text prompts, foster innovation through historical novelty, and seek diversity by identifying unique configurations. ASAL’s adoption ushers in a scalable and innovative approach to ALife research, moving beyond manual methods, thereby setting the stage for further exploration and discovery facilitated by foundation models.